|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .circleci | ||
| Assets | ||
| ProjectSettings | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
README.md
UniTask
Provides an efficient async/await integration to Unity.
UniTask was included in UniRx before v7 but now completely separated, it no dependent each other.
Getting started
Install package(UniRx.Async.unitypackage) is available in UniTask/releases page.
// extension awaiter/methods can be used by this namespace
using UniRx.Async;
// You can return type as struct UniTask<T>(or UniTask), it is unity specialized lightweight alternative of Task<T>
// no(or less) allocation and fast excution for zero overhead async/await integrate with Unity
async UniTask<string> DemoAsync()
{
// You can await Unity's AsyncObject
var asset = await Resources.LoadAsync<TextAsset>("foo");
// .ConfigureAwait accepts progress callback
await SceneManager.LoadSceneAsync("scene2").ConfigureAwait(Progress.Create<float>(x => Debug.Log(x)));
// await frame-based operation like coroutine
await UniTask.DelayFrame(100);
// replacement of WaitForSeconds/WaitForSecondsRealtime
await UniTask.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10), ignoreTimeScale: false);
// replacement of WaitForEndOfFrame(or other timing like yield return null, yield return WaitForFixedUpdate)
await UniTask.Yield(PlayerLoopTiming.PostLateUpdate);
// replacement of yield return WaitUntil
await UniTask.WaitUntil(() => isActive == false);
// You can await IEnumerator coroutine
await FooCoroutineEnumerator();
// You can await standard task
await Task.Run(() => 100);
// Multithreading, run on ThreadPool under this code(use SwitchToMainThread, same as `ObserveOnMainThreadDispatcher`)
await UniTask.SwitchToThreadPool();
// get async webrequest
async UniTask<string> GetTextAsync(UnityWebRequest req)
{
var op = await req.SendWebRequest();
return op.downloadHandler.text;
}
var task1 = GetTextAsync(UnityWebRequest.Get("http://google.com"));
var task2 = GetTextAsync(UnityWebRequest.Get("http://bing.com"));
var task3 = GetTextAsync(UnityWebRequest.Get("http://yahoo.com"));
// concurrent async-wait and get result easily by tuple syntax
var (google, bing, yahoo) = await UniTask.WhenAll(task1, task2, task3);
// You can handle timeout easily
await GetTextAsync(UnityWebRequest.Get("http://unity.com")).Timeout(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(300));
// return async-value.(or you can use `UniTask`(no result), `UniTaskVoid`(fire and forget)).
return (asset as TextAsset)?.text ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Asset not found");
}
UniTask<T>
UniTask feature rely on C# 7.0(task-like custom async method builder feature) so required Unity version is after Unity 2018.3.
Why UniTask(custom task-like object) is required? Because Task is too heavy, not matched to Unity threading(single-thread). UniTask does not use thread and SynchronizationContext because almost Unity's asynchronous object is automaticaly dispatched by Unity's engine layer. It acquires more fast and more less allocation, completely integrated with Unity.
More details, please see this slide: Deep Dive async/await in Unity with UniTask(EN)
You can await AsyncOperation, ResourceRequest, UnityWebRequestAsyncOperation, IEnumerator and others when using UniRx.Async.
UniTask.Delay, UniTask.Yield, UniTask.Timeout that is frame-based timer operators(no uses thread so works on WebGL publish) driven by custom PlayerLoop(Unity 2018 experimental feature). In default, UniTask initialize automatically when application begin, but it is override all. If you want to append PlayerLoop, please call PlayerLoopHelper.Initialize(ref yourCustomizedPlayerLoop) manually.
Before Unity 2019.3, Unity does not have
PlayerLooop.GetCurrentPlayerLoopso you can't use with Unity ECS package in default. If you want to use with ECS and before Unity 2019.3, you can use this hack below.
// Get ECS Loop.
var playerLoop = ScriptBehaviourUpdateOrder.CurrentPlayerLoop;
// Setup UniTask's PlayerLoop.
PlayerLoopHelper.Initialize(ref playerLoop);
UniTask.WhenAll, UniTask.WhenAny is like Task.WhenAll/WhenAny but return type is more useful.
UniTask.ctor(Func<UniTask>) is like the embeded AsyncLazy<T>
public class SceneAssets
{
public readonly UniTask<Sprite> Front;
public readonly UniTask<Sprite> Background;
public readonly UniTask<Sprite> Effect;
public SceneAssets()
{
// ctor(Func) overload is AsyncLazy, initialized once when await.
// and after it, await returns zero-allocation value immediately.
Front = new UniTask<Sprite>(() => LoadAsSprite("foo"));
Background = new UniTask<Sprite>(() => LoadAsSprite("bar"));
Effect = new UniTask<Sprite>(() => LoadAsSprite("baz"));
}
async UniTask<Sprite> LoadAsSprite(string path)
{
var resource = await Resources.LoadAsync<Sprite>(path);
return (resource as Sprite);
}
}
If you want to convert callback to UniTask, you can use UniTaskCompletionSource<T> that is the lightweight edition of TaskCompletionSource<T>.
public UniTask<int> WrapByUniTaskCompletionSource()
{
var utcs = new UniTaskCompletionSource<int>();
// when complete, call utcs.TrySetResult();
// when failed, call utcs.TrySetException();
// when cancel, call utcs.TrySetCanceled();
return utcs.Task; //return UniTask<int>
}
You can convert Task -> UniTask: AsUniTask, UniTask -> UniTask<AsyncUnit>: AsAsyncUnitUniTask(this is useful to use WhenAll/WhenAny), UniTask<T> -> UniTask: AsUniTask.
If you want to convert async to coroutine, you can use UniTask.ToCoroutine, this is useful to use only allow coroutine system.
Cancellation and Exception handling
Some UniTask factory methods have CancellationToken cancellation = default(CancellationToken) parameter. Andalso some async operation for unity have ConfigureAwait(..., CancellationToken cancellation = default(CancellationToken)) extension methods.
You can pass CancellationToken to parameter by standard CancellationTokenSource.
var cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
cancelButton.onClick.AddListener(() =>
{
cts.Cancel();
});
await UnityWebRequest.Get("http://google.co.jp").SendWebRequest().ConfigureAwait(cancellation: cts.Token);
await UniTask.DelayFrame(1000, cancellationToken: cts.Token);
CancellationToken can create by CancellationTokenSource or MonoBehaviour's extension method GetCancellationTokenOnDestroy.
// this CancellationToken lifecycle is same as GameObject.
await UniTask.DelayFrame(1000, cancellationToken: this.GetCancellationTokenOnDestroy());
When detect cancellation, all methods throws OperationCanceledException and propagate to upstream. OperationCanceledException is special exception, if not handled this exception, finally it is propagated to UniTaskScheduler.UnobservedTaskException.
Default behaviour of received unhandled exception is write log as warning. Log level can change by UniTaskScheduler.UnobservedExceptionWriteLogType. If you want to change custom beavhiour, set action to UniTaskScheduler.UnobservedTaskException.
If you want to cancel behaviour in async UniTask method, throws OperationCanceledException manually.
public async UniTask<int> FooAsync()
{
await UniTask.Yield();
throw new OperationCanceledException();
}
If you handle exception but want to ignore(propagete to global cancellation handling), use exception filter.
public async UniTask<int> BarAsync()
{
try
{
var x = await FooAsync();
return x * 2;
}
catch (Exception ex) when (!(ex is OperationCanceledException))
{
return -1;
}
}
throws/catch OperationCanceledException is slightly heavy, if you want to care performance, use UniTask.SuppressCancellationThrow to avoid OperationCanceledException throw. It returns (bool IsCanceled, T Result) instead of throw.
var (isCanceled, _) = await UniTask.DelayFrame(10, cancellationToken: cts.Token).SuppressCancellationThrow();
if (isCanceled)
{
// ...
}
Note: Only suppress throws if you call it directly into the most source method.
Progress
Some async operation for unity have ConfigureAwait(IProgress<float> progress = null, ...) extension methods.
var progress = Progress.Create<float>(x => Debug.Log(x));
var request = await UnityWebRequest.Get("http://google.co.jp")
.SendWebRequest()
.ConfigureAwait(progress: progress);
Should not use new System.Progress<T>, because it allocate every times. Use UniRx.Async.Progress instead. Progress factory has two methods, Create and CreateOnlyValueChanged. CreateOnlyValueChanged calls only when progress value changed. Should not use new System.Progress<T>, it allocate every times.
Implements interface is more better.
public class Foo : MonoBehaviour, IProgress<float>
{
public void Report(float value)
{
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(value);
}
public async UniTaskVoid WebRequest()
{
var request = await UnityWebRequest.Get("http://google.co.jp")
.SendWebRequest()
.ConfigureAwait(progress: this); // pass this
}
}
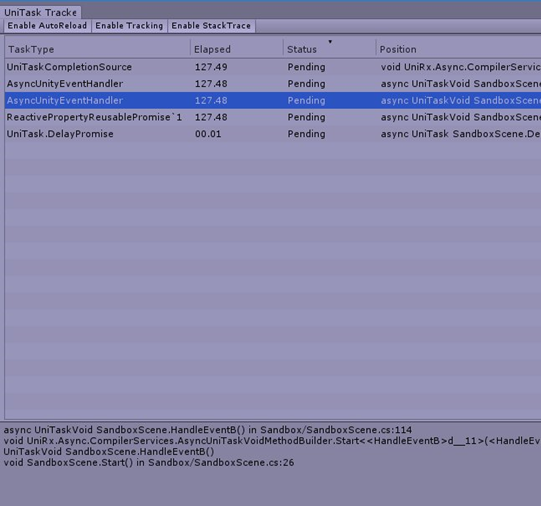
UniTaskTracker
useful for check(leak) UniTasks. You can open tracker window in Window -> UniTask Tracker.
- Enable AutoReload(Toggle) - Reload automatically.
- Reload - Reload view.
- GC.Collect - Invoke GC.Collect.
- Enable Tracking(Toggle) - Start to track async/await UniTask. Performance impact: low.
- Enable StackTrace(Toggle) - Capture StackTrace when task is started. Performance impact: high.
For debug use, enable tracking and capture stacktrace is useful but it it decline performance. Recommended usage is enable both to find task leak, and when done, finally disable both.
Reusable Promises
Some UniTask factory can reuse to reduce allocation. The list is Yield, Delay, DelayFrame, WaitUntil, WaitWhile, WaitUntilValueChanged.
var reusePromise = UniTask.DelayFrame(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
await reusePromise;
}
awaitable Events
Unity events can await like OnClickAsync, OnCollisionEnterAsync. It can use by UniRx.Async.Triggers.
using UniRx.Async.Triggers;
async UniTask TripleClick(CancellationToken token)
{
await button.OnClickAsync(token);
await button.OnClickAsync(token);
await button.OnClickAsync(token);
Debug.Log("Three times clicked");
}
// more efficient way
async UniTask TripleClick(CancellationToken token)
{
using (var handler = button.GetAsyncClickEventHandler(token))
{
await handler.OnClickAsync();
await handler.OnClickAsync();
await handler.OnClickAsync();
Debug.Log("Three times clicked");
}
}
async void vs async UniTask/UniTaskVoid
async void is standard C# system so does not run on UniTask systems. It is better not to use. async UniTaskVoid is lightweight version of async UniTask because it does not have awaitable completion. If you don't require to await it(fire and forget), use UniTaskVoid is better. Unfortunately to dismiss warning, require to using with Forget().
For Unit Testing
Unity's [UnityTest] attribute can test coroutine(IEnumerator) but can not test async. UniTask.ToCoroutine bridges async/await to coroutine so you can test async method.
[UnityTest]
public IEnumerator DelayIgnore() => UniTask.ToCoroutine(async () =>
{
var time = Time.realtimeSinceStartup;
Time.timeScale = 0.5f;
try
{
await UniTask.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3), ignoreTimeScale: true);
var elapsed = Time.realtimeSinceStartup - time;
Assert.AreEqual(3, (int)Math.Round(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(elapsed).TotalSeconds, MidpointRounding.ToEven));
}
finally
{
Time.timeScale = 1.0f;
}
});
Method List
UniTask.WaitUntil
UniTask.WaitWhile
UniTask.WaitUntilValueChanged
UniTask.SwitchToThreadPool
UniTask.SwitchToTaskPool
UniTask.SwitchToMainThread
UniTask.SwitchToSynchronizationContext
UniTask.Yield
UniTask.Run
UniTask.Lazy
UniTask.Void
UniTask.ConfigureAwait
UniTask.DelayFrame
UniTask.Delay(..., bool ignoreTimeScale = false, ...) parameter
UPM Package
After Unity 2019.3.4f1, Unity 2020.1a21, that support path query parameter of git package. You can add https://github.com/Cysharp/UniTask.git?path=Assets/UniRx.Async to Package Manager
or add "com.cysharp.unitask": "https://github.com/Cysharp/UniTask.git?path=Assets/UniRx.Async" to Packages/manifest.json.
If you want to set a target version, UniTask is using *.*.* release tag so you can specify a version like #1.3.0. For example https://github.com/Cysharp/UniTask.git?path=Assets/UniRx.Async#1.3.0.
License
This library is under the MIT License.